숟가락 그만 얹어
Epistemic vs. Aleatoric 본문
Uncertainty 관련 논문들에서 언급되는 epstemic과 aleatoric uncertainty를 다시 정리해보고자 한다. 첫 번째로 uncertainty에 대한 모델링은 아래 predictive distributuon에 대한 entropy로 정의 가능하다.
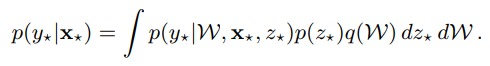
위 식에서 randomness는 p(z)로부터 발생하는 noise와 W ~ q(W)에 기인한다. p(z)는 observation에 내재된 noise로 irreducible하며 (aleatoric), q(W)는 더 많은 데이터의 수집으로 approximation을 잘하면 randomness를 줄일 수 있다.
두 번째로 epistemic과 aleatoric은 mutual information 식으로도 표현이 가능한데,
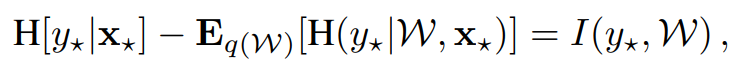
좌변의 첫 번째 term은 predictive distribution의 entropy로서 uncertainty의 총량을 나타낸다. 두 번째 term의 경우 W에 따른 영향을 없앤 entropy로 p(z)의 영향만을 고려한, aleatoric에 해당한다. 우변에 해당하는 term은 y가 W에 의해 결정되어 버리면 (x에 의해 결정되어야 한다) 모델의 confidence가 낮은 것으로 해석할 수 있다.
왜 그럴까?
Aleatoric uncertainty는 error와 관련이 있다. 어떤 model의 output으로 Softmax 또는 Gaussian likelihood로 설정된 경우 ground truth와의 error가 클수록 uncertainty (probability 또는 variance)가 커진다. 이는 어쨌든 in-distribution에서의 error이므로 out-of-distribution sample의 경우는 어떤 behavior를 보일지 알 수 없다. 이 외의 model을 구성하는 다른 것들은 전체 training set distribution에 대한 distribution(?)을 조절하는 요소라고 생각할 수 있겠다 (not clear).
References
[1] L. Smith et al., Understanding Measures of Uncertainty for Adversarial Example Detection, UAI 2018
[2] A. Kendall et al., What Uncertainties Do We Need in Bayesian Deep Learning for Computer Vision?, NIPS 2017
'Research > Uncertainty' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Deep Deterministic Uncertainty (0) | 2021.05.31 |
|---|---|
| Prior Networks (0) | 2020.12.01 |
| What Uncertainties Do We Need? (0) | 2020.09.08 |
| Can you trust your model's uncertainty? (0) | 2020.08.22 |
| Deep Ensembles (0) | 2020.08.21 |


